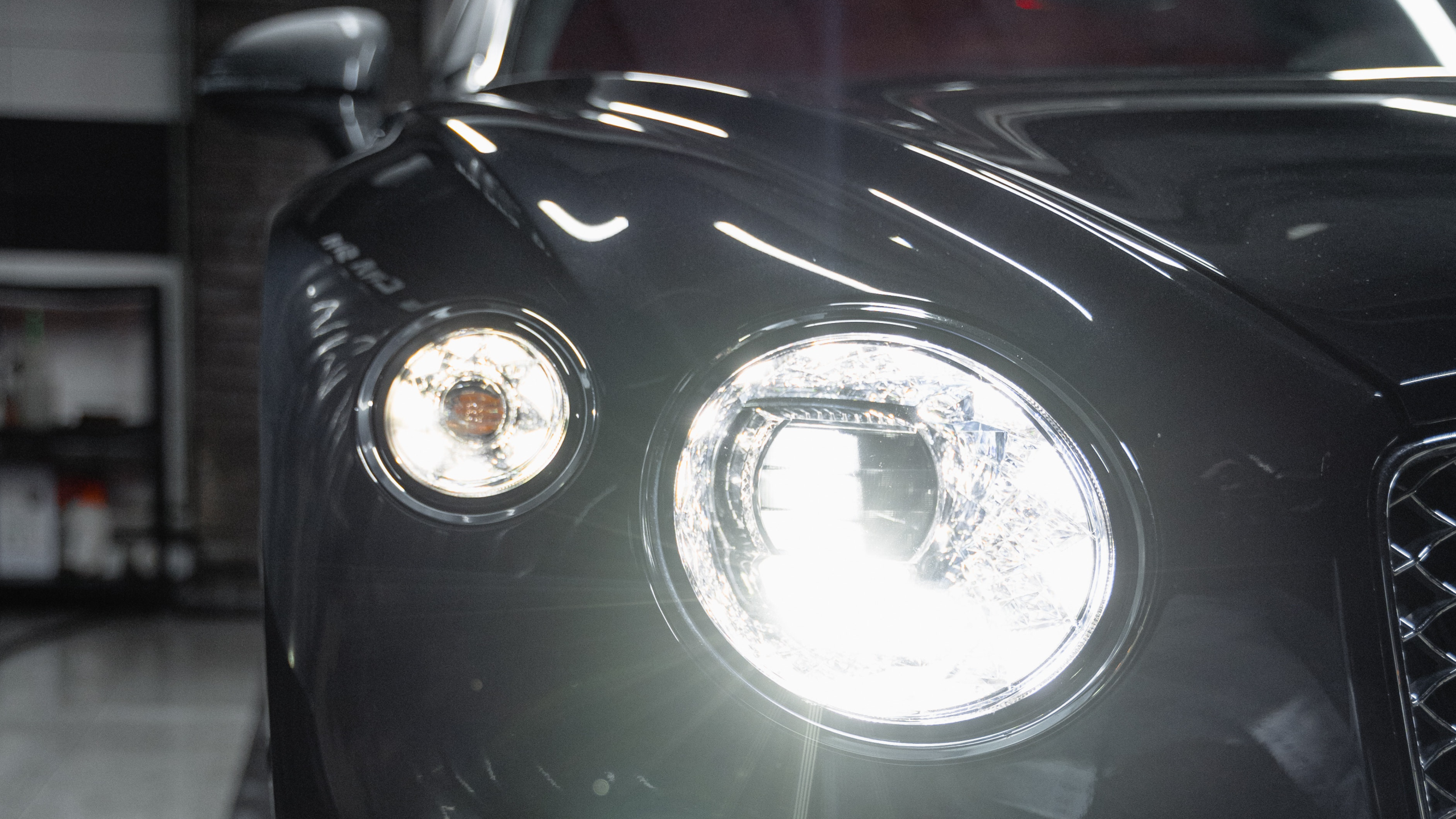
It wasn’t that long ago that headlights were a part of your car that didn’t require any thought, until a globe went. All cars had them and no one really paid them much attention.
Historically, tungsten filaments, similar to the kind found in household light bulbs, were finally settled on as the norm for virtually all cars. From the mid-1960s until now these tungsten filaments have been encased in a bubble of halogen gas in order to improve performance and longevity.
For much of their history, tungsten and halogen lamps focused light on the road via a lens that doubled as the headlight’s protective housing; now the two jobs are quite separate. Since the 90s the exterior casings of headlights have been made from polycarbonate instead glass because it is both lighter and stronger, while light from the headlamp bulb is aimed via a series of complex reflectors. Alternatively, the light beam can be directed by a projector lens within the headlight housing.
Combing low cost and a working life of between 500 and 1000 hours, halogen bulbs are the most common headlamp type in use today, although that is rapidly changing. Moving things along is the car makers efforts to improve efficiency. Halogen bulbs draw around 55 watts of power, and much of that is wasted as it’s converted into heat rather than light.
Light emitting diodes (LEDs) have come a long way from the simple flashing lights on computers to being key components in modern cars, phones and televisions.
They provide most of the lighting used in today’s instrument panels, entertainment head units and car interiors. Arrays of these diodes are used in fog lamps, indicators and brake lights. Car designers use LEDs because their small size allows them to be fashioned into thinner and more design-styled shapes. Although LED headlights currently fall a little short of the brightness achieved by HIDs, they hit maximum brightness within a millionth of a second compared with the half second required by incandescent and halogen lights. When LEDs are used in brake and indicator lights some bulb makers are claiming a life of up to 15,000 hours for their LED headlamps.
Touch a halogen bulb or xenon globe when it’s on and you will get burnt from the heat, but with LED headlights this is not the case. This is their great advantage, they convert most of the energy directed to them into light not heat. In-fact, most of the heat generated by LEDs is at their electrical base, not on the bulb surface.
For the last few years LED headlights were only available in high-end cars. Recent advances have fixed any earlier problems regarding brightness and rearward heat dissipation, and LED headlights are now the mainstream in newer vehicles. The latest cars’ brighter nights and smoother new styling is down to tiny LEDs. The tiny Light Emitting Diode (LED) is powering the biggest revolution in after-dark driving since cars hit the road more than 120 years ago.
Their rapid take-up is a big bonus for drivers, but they also cut power needs (good for EVs), allow slimmer lamps and provide designers with more flexibility and opportunity for styling and brand identification.
Newer Headlight Globe Benefits
If more efficient, brighter, headlights has you thinking of ways to upgrade your current older vehicle’s lights, there are good replacements these days that will fit the bill. Lighting Efficiency, better vision, more efficient are just some of the benefits when compared to older globes. LED headlights are built with greater strength and efficiency compared to halogen bulbs of the past.
Longer lifespan made with high quality materials. Through continuous use, this type of headlight can last for eleven to twenty-two years. That is comparatively more efficient than the ordinary halogen light bulb. LED lights are less prone to failures or discrepancies than halogen bulbs because it is typically made out of high-grade materials that are up to the standards of a quality controlling governing body.
Modern globe replacements come with some advanced engineering to create a better product. The LED itself is a light source. It’s superior to Halogen or Xenon gas, mainly in efficiency. It’s also the way it emits the light, in a cone. Because the light is emitted in one direction, you can use it more efficiently. There is also a lot less heat, so you can package the light sources closer together to create a matrix system. Ultimately, there are numerous choices and with that some advice is advisable. In addition, they can be complex to fit.
You can rely on our experience
Some of the newer technology in globe replacements offer many advantages to vehicles either on or off the road and Autospark have always been at the forefront of the latest innovations.
Autospark stocks a range of the most popular and best of brand versions to choose from like Hella, Narva and Philips and they are experts at fitting them for you too. If you need advice, you can always rely on the professionals at Autospark for the best in Globe Replacements for your vehicle.